Introduction
From GPS in smartphones to tracking trains and monitoring satellites, space communication and navigation systems are powering much of our modern life. These systems support vital services like TV broadcasting, military surveillance, weather forecasting, and disaster alerts.
Globally, this sector is growing fast. India, backed by ISRO and new-age private companies, is also stepping up in a big way. Space communication and navigation systems in India are evolving beyond basic support functions. They are now becoming critical to the country’s defense, connectivity, and commercial ambitions.
India is not just launching satellites anymore. It is building home-grown satellite constellations, developing its own navigation system (NavIC), and expanding deep-space communication infrastructure. The country aims to capture a significant share of the global space economy, which is expected to touch trillions of dollars in the coming years.
In this blog, we’ll break down the global growth of space systems, India’s rising role, and the top listed companies leading this transformation.
Global Market Outlook for Space Communication and Navigation Systems
The global demand for space communication and navigation systems is on a rapid upward trajectory. As satellite networks, space-based GPS alternatives, and advanced communication payloads become more vital across sectors, the global space economy is scaling new heights.
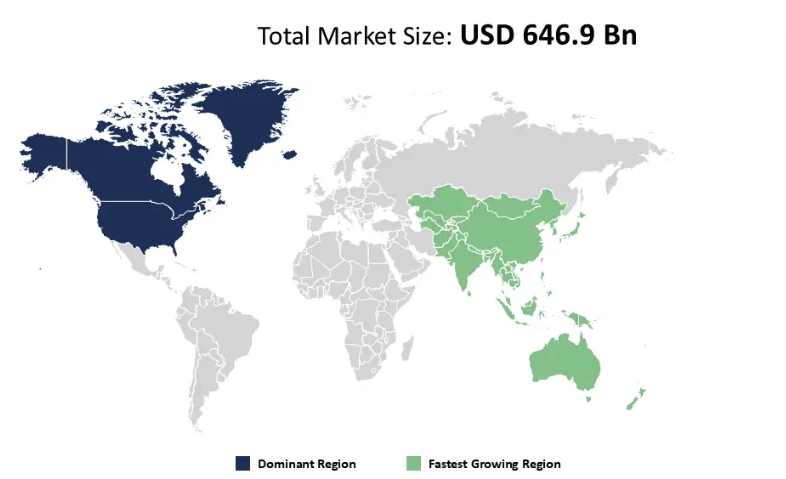
In 2025, the global space economy is estimated to be worth USD 646.90 billion. By 2032, it is expected to more than double to USD 1.4 trillion, growing at a CAGR of 11.7%. Another forecast projects it will reach USD 1.8 trillion by 2035, up from USD 630 billion in 2023. A major portion of this surge will be driven by satellite communication systems, which currently dominate the market.
Satellite Industry: The Backbone of Global Space Communication
As of 2024, satellites accounted for over 71% of the global space economy, making it the largest segment. These satellites enable everything from internet access and mobile communication to precise navigation services for air, land, and sea.
Growth in Space Infrastructure and Navigation Segments
The space infrastructure market, which includes ground stations, launch systems, and communication architecture, is expected to grow from USD 148.80 billion in 2024 to USD 307.41 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.68%.
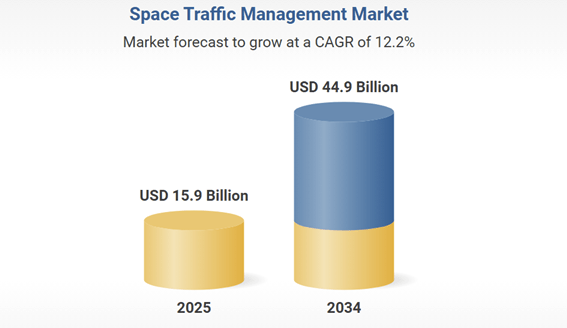
Meanwhile, the Space Traffic Management (STM) market, which covers advanced space navigation technologies and collision avoidance systems, is projected to expand from USD 15.9 billion in 2025 to USD 44.9 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.2%. This segment will become increasingly important as the number of satellites in orbit grows exponentially.
India’s Booming Space Economy and Role in Global Navigation & Communication
While the global space industry is booming, India is rapidly emerging as a serious force in space communication and navigation systems. Fueled by government reforms, ISRO’s expanding mission portfolio, and rising private participation, the country is now actively scaling its space economy.
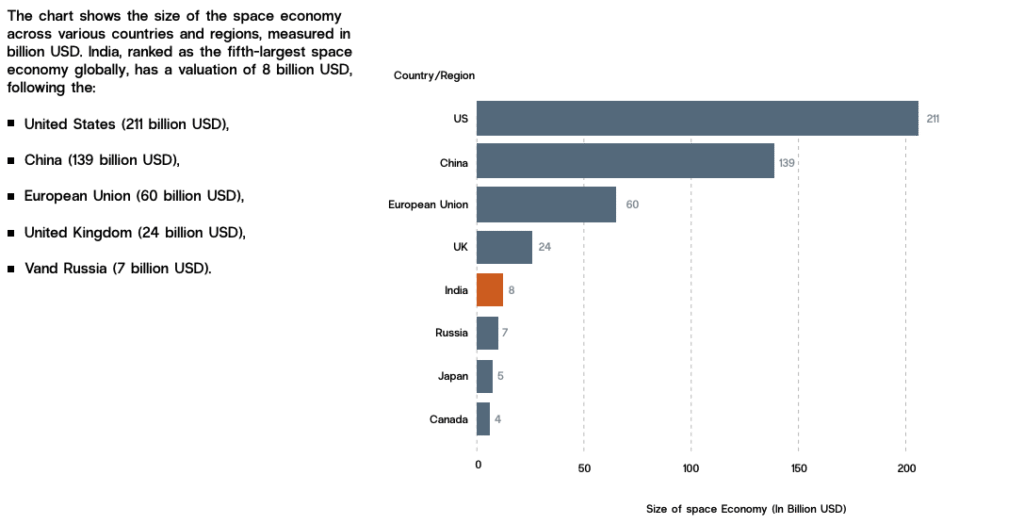
India’s space economy stood at $8.4 billion in 2022, but it’s not staying small for long. By 2033, it is expected to grow more than fivefold to $44 billion. Notably, India aims to capture 8% of the global space market by that time — a huge leap from its current share.
Satellite Communication: A Major Growth Engine
One of the key pillars of this growth is satellite communication. This segment alone is predicted to contribute $14.8 billion to India’s space economy by 2033. In fact, the satellite communication market in India is projected to grow from US$ 3,509.6 million in 2024 to US$ 5,942.7 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 9.2%.
Currently, services like satellite TV and broadband dominate the space. However, the equipment segment is catching up quickly, with innovations in ground terminals, antennas, and space hardware.
Space Radar and Navigation Market in India
Beyond satellites, navigation and radar-based systems are also gaining traction. India’s space radar market, which overlaps with navigation technologies, is expected to jump from US$ 30 million in 2024 to US$ 96.7 million by 2033 — growing at a CAGR of 13.9%.
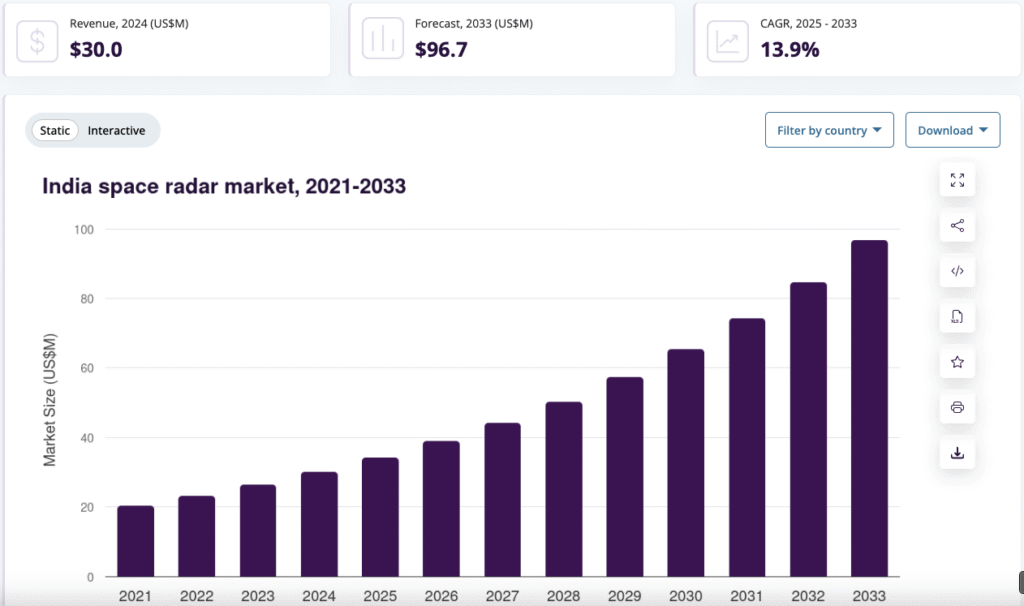
As of 2024, India already accounted for 4.6% of the global space radar market, and this share is likely to grow. With programs like NavIC, ISRO’s indigenous navigation system, India is not just a user but a creator of global navigation alternatives.
Transitioning from Dependency to Leadership
Earlier, India largely depended on foreign systems like GPS for navigation and communications. Now, space communication and navigation systems in India are becoming indigenous, scalable, and export-ready. This shift positions India as a future hub for affordable, reliable space solutions in both the commercial and strategic domains.
Top Listed Indian Companies Driving Space Communication and Navigation Systems
India’s journey in space is no longer limited to launching satellites. The focus has now shifted to building an indigenous ecosystem for space communication and navigation systems—both in space and on the ground. Several publicly listed companies have stepped up to fill this strategic gap, playing pivotal roles in satellite communication terminals, navigation payloads, radar systems, and launch vehicle integration.
Let’s take a closer look at these companies—their past contributions, future contracts, and strategic alignment with India’s space goals.
1. MTAR Technologies Ltd
Core Focus: Launch vehicle propulsion and structural systems (indirect enablers for communication/navigation payloads)
Key Contributions:
- Supplied mission-critical assemblies for ISRO’s PSLV-C25 (Mangalyaan), PSLV-C49 (EOS-01), and GSLV Mark III (Chandrayaan II).
- Delivered components like liquid propulsion engines, cryogenic engine systems, reaction wheels, momentum wheels, and redundant valves—vital for stabilizing and controlling satellites carrying communication payloads.

Recent Developments:
- Received fresh orders worth ₹1.38 crore from ISRO in 2024.
- In FY24, aerospace and defense contributed 38% of MTAR’s total revenue, and this share is set to rise due to new ISRO and global aerospace contracts.
Why It Matters: While MTAR doesn’t directly build communication systems, its propulsion hardware is essential to placing such payloads into orbit with precision.
2. Avantel Ltd
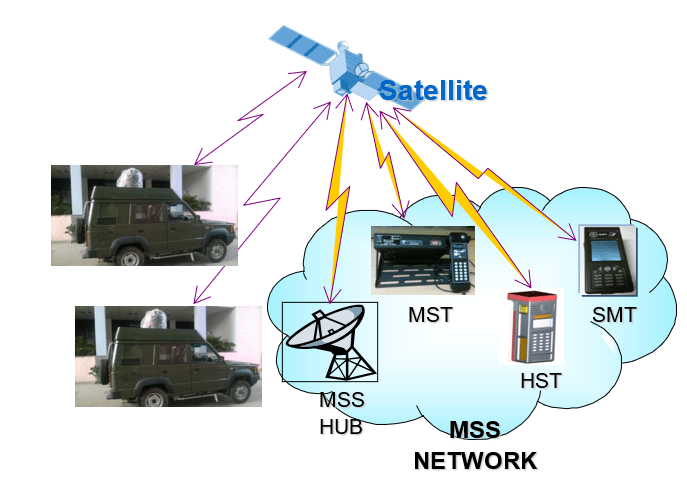
Core Focus: Indigenous SATCOM equipment, mobile satellite services, and defense communication terminals.
Key Contributions:
- Developed GSAT-based Mobile Satellite Services (MSS) solutions for military and maritime users.
- Created SATCOM Radios for S and UHF bands, widely deployed by defense forces.
- Received technology transfers from ISRO for ground station systems including:
- S/X/Ka tri-band feed systems
- Tri-axis antenna control
- Ku/C/L and S-band Cassegrain antennas
- Built RTIS (Real-time Train Information System) for Indian Railways using GPS/GIS/MSS technologies.

Future Outlook:
- Shortlisted for a ₹500 crore ISRO project to extend satellite connectivity to remote areas over 5 years.
- Finalizing a ₹300 crore defense contract for SATCOM systems.
- Recently won an ₹11.37 crore order from Goa Shipyard Ltd for outfitting Indian Navy’s NGOPV ships with secure satellite communication modules.
Why It Matters: Avantel is one of the very few Indian companies actively working on end-to-end SATCOM systems, including terminals, ground stations, and field-level integration—directly enabling space-based communication infrastructure.
3. Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL)
Core Focus: Ground-based satellite systems, navigation receivers (IRNSS/NavIC), satellite payloads, and strategic electronics.
Key Contributions:
- Developed IRNSS (NavIC) receivers in various form factors for commercial and defense navigation use.
- Participated in AIT (Assembly, Integration, Testing) of ISRO’s RISAT-1, RISAT-2, and RISAT-2BR1—key for earth observation and data relay.
- Manufactures ground SATCOM systems including:
- Manpack terminals
- Satcom-on-the-Move (SoTM) systems
- Ground terminals for defense communication
- Fixed and transportable satellite hubs
Strategic Developments:
- Signed a Teaming Agreement with Canada’s Reliasat Inc. to develop telecom and micro-satellites for global markets.
- Developing a LEO satellite constellation based on ISRO’s Technology Transfer (ToT).
- Expressed intent to co-produce Satellite Launch Vehicles under the Make-in-India initiative.
- Recently received ₹537 crore worth of strategic orders for naval communication and composite electronics systems.
Why It Matters: BEL combines decades of defense electronics experience with cutting-edge satellite and navigation technology, positioning itself as India’s top state-owned enabler for both civil and military satellite systems.
4. Data Patterns (India) Ltd
Core Focus: End-to-end satellite subsystems, payload electronics, ground control infrastructure, and test automation for space hardware.
Key Contributions:
- Designed off-the-shelf Nano Satellite Bus for NIUSAT, INS-1A, INS-1B, and INS-1C with:
- TTC Transceivers
- Downlink payloads
- Star Sensors, Sun Sensors, GPS Modules
- Magnetometers, ADCS algorithms, and Reaction Wheels
- Built open-frame ground stations compatible with VHF, UHF, and S-band frequencies.
- Developed Automated Test Equipment (ATE) for ISRO’s PSLV and GSLV programs.

Strategic Edge:
- Approved ISRO vendor with a proven space-qualified product line.
- Developed a spread spectrum modem for both terrestrial and satellite communication under defense protocols.
- Positioned to support upcoming LEO and CubeSat launches from India’s small satellite missions.
Why It Matters: Data Patterns delivers both onboard satellite electronics and ground infrastructure, offering full-stack capability for communication and navigation operations.
5. Larsen & Toubro (L&T)
Core Focus: Deep space tracking infrastructure, launch vehicle systems, SATCOM hardware, and radar installations.
Key Contributions:
- Installed India’s 32-meter deep space antenna at Byalalu (part of ISRO’s Indian Deep Space Network).
- Supplied Precision Monopulse Tracking Radars (PMTRs) for SDSC SHAR and ISRO’s Bengaluru facility.
- Delivered the HS200 booster segment for ISRO’s Gaganyaan (LVM3) crewed launch vehicle.
- Developed ground-based SATCOM infrastructure including dish installations, radomes, and telemetry hardware.

What’s Next:
- Likely to support NASA-ISRO NISAR mission launching in July 2025.
- Expected to continue hardware support for the Gaganyaan program, especially in critical navigation and reentry tracking systems.
Why It Matters: L&T is a key infrastructure partner, supporting the physical foundation of India’s navigation and communication network—from launchpads to radars.
6. Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL)
Core Focus: Rocket and satellite platform manufacturing, propulsion systems, and complete SSLV production.
Key Contributions:
- Built vital components for PSLV, GSLV, and Chandrayaan missions, including cryogenic engines, propellant tanks, and structural assemblies.
- Integral to Gaganyaan’s launch vehicle architecture.

Major Shift:
- In 2024, HAL became the first Indian company to receive full technology transfer from ISRO to build and launch the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) under NSIL.
- NSIL expects 6–8 SSLV launches per year, scaling to 10 as demand for small, low-orbit satellites grows.
- SSLVs are expected to carry payloads for satellite communication, IoT, and regional navigation systems, especially for military surveillance under the SBS-III program (52 new satellites).
Why It Matters: HAL’s entry into full satellite launch operations transforms it from a component supplier to a vertically integrated space launch provider.
Together, these companies form the backbone of space communication and navigation systems in India. Their innovations, strategic contracts, and growing global relevance are transforming India from a spacefaring nation into a space technology powerhouse.
India’s Space Communication & Navigation: Why It Matters and What’s Next
India’s space tech isn’t just about launching rockets anymore. Today, space communication and navigation systems in India play a key role in defense, transport, disaster alerts, farming, and even mobile connectivity.
NavIC: India’s Own GPS
Instead of depending on foreign systems like GPS, India is now pushing NavIC—our own navigation system. It already helps track military equipment, trains, ships, and even weather patterns. Soon, it will be added to all smartphones and cars sold in India.
Defense and Satellites Working Together
Satellite-based communication is now crucial for our army, navy, and air force. For example:
- The Navy uses satellite links to monitor oceans.
- The Army uses GPS-like signals for border operations.
- New military satellites are being launched for surveillance and tracking.
Companies like BEL, Avantel, and HAL are building much of this tech in partnership with ISRO.
Big Opportunities Ahead
India’s space sector is opening up for private players. ISRO is now working with companies like L&T, MTAR, and Data Patterns to build satellites, launch vehicles, and ground stations. This means:
- More jobs
- More exports
- And more investment opportunities for retail investors
With the global space economy set to cross $1 trillion in the next two decades, India is preparing to grab a big share.
Conclusion: India’s Space Future Is Taking Off
India is no longer just a follower in space tech—it’s becoming a serious player. From building its own NavIC navigation system to launching communication satellites that support defense, transport, and disaster management, India is setting big goals and backing them with real progress.
With strong government support, rising private-sector innovation, and a growing list of satellite applications, the space communication and navigation systems in India are ready to power the next wave of growth. For investors, engineers, and even everyday citizens, the sky is no longer the limit—it’s just the beginning.
FAQs on space communication and navigation systems in India
What is NavIC and how do people use it in India?
NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) provides accurate location data across India. People use it in smartphones, vehicles, disaster alerts, and defense systems.
How does NavIC differ from GPS?
NavIC offers better accuracy in India and nearby regions, while GPS serves globally. NavIC also ensures more secure and region-specific navigation.
Which Indian companies build space communication systems?
Companies like BEL, Avantel, HAL, L&T, Data Patterns, and MTAR Technologies build satellites, antennas, and ground systems for ISRO and defense projects.
What role does ISRO play in communication satellites?
ISRO designs, develops, and launches satellites like GSAT and IRNSS to power telecom, TV broadcasting, navigation, and defense communication.
How does satellite communication support India’s defense?
Defense forces use satellite communication to coordinate missions, track assets, guide weapons, and share real-time intelligence across all branches.
How large is India’s satellite communication market?
The market could grow to $5.9 billion by 2030, driven by defense demand, telecom growth, and private-sector innovation.
How do civilians benefit from India’s navigation systems?
People use NavIC for accurate navigation, fleet tracking, railway timing, emergency alerts, farming guidance, and mobile apps.
How is India reducing dependence on GPS?
India integrates NavIC into mobile chips, defense tools, and transport systems to cut reliance on foreign navigation systems like GPS.
How does the private sector contribute to this space?
Private firms supply ISRO with components, develop satellite technologies, and run ground operations for navigation and communication systems.
What lies ahead for India’s space communication sector?
The sector will expand fast as the government pushes self-reliance, ISRO collaborates with startups, and global demand for space tech rises.
Related Articles
Space Stock: Indian Companies Set to Soar
Indian Biotechnology Sector: A $300 Billion Opportunity in the Making
Defence Stocks After the Rally: Hold, Book Profits, or Buy the Dip?