Introduction: How Technology is Changing the Way We Trade
Imagine a world where trades are executed in milliseconds, decisions are made without human bias, and strategies are tested against years of market data. Welcome to algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading—a revolutionary way to participate in the stock market. While algo trading was once reserved for large institutions, it is now becoming increasingly accessible to retail investors thanks to advancements in technology and brokerage platforms. In this guide, we’ll explore what algo trading is, how it works, and how you can get started.
What is Algo Trading?
Algorithmic trading refers to the use of computer programs and algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria, such as price, volume, timing, or other mathematical models. The goal is to maximize efficiency and minimize human error.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Speed | Trades are executed in fractions of a second, often faster than human capability. |
| Automation | Eliminates manual intervention by automating decision-making and trade execution. |
| Precision | Trades are executed at the best possible prices with minimal slippage. |
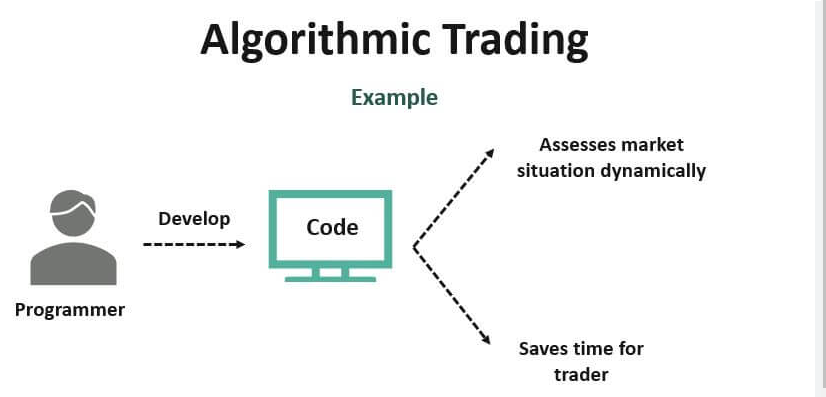
How Does Algo Trading Work?
Algo trading relies on three key components:
- Algorithms: Predefined rules and mathematical models determine when and how trades are executed.
- Data Feeds: Real-time market data is essential for accurate decision-making.
- Execution Platforms: Trades are executed automatically through APIs connected to stock exchanges.
Suppose you set an algorithm to buy a stock when its 50-day moving average crosses above its 200-day moving average (a bullish signal). The program will monitor the market and execute the trade as soon as the condition is met.
Advantages of Algo Trading
1. Eliminates Emotional Bias
Human traders often make impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. Algorithms operate purely on logic and data, removing emotional interference.
2. Backtesting Strategies
Algo trading allows you to test strategies on historical data to evaluate their effectiveness before risking real money.
3. Increased Speed and Efficiency
Algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and execute trades in milliseconds, ensuring you never miss an opportunity.
4. Consistency
Algorithms follow the same set of rules without deviation, ensuring consistency in trading behavior.

Challenges and Risks of Algo Trading
1. Technical Complexity
Developing and maintaining algorithms require programming skills and a deep understanding of markets.
2. High Initial Costs
While retail platforms are making algo trading more affordable, initial setup costs, including software and APIs, can still be high.
3. Over-Optimization
Over-reliance on backtesting can lead to strategies that perform well on historical data but fail in live markets.
4. System Failures
Technical glitches or connectivity issues can disrupt automated trading systems, leading to unexpected losses.

Popular Strategies in Algo Trading
1. Arbitrage
Arbitrage involves exploiting price differences for the same asset in different markets. For example, if a stock is priced at ₹1,000 on the NSE and ₹1,005 on the BSE, an algorithm can simultaneously buy on the NSE and sell on the BSE to pocket the ₹5 difference per share. This strategy requires high-speed execution and accurate data feeds to capitalize on these fleeting opportunities.
2. Trend Following
Trend-following strategies identify and trade in the direction of the market trend. Indicators like moving averages, MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and Bollinger Bands are commonly used. For instance, a trader might use an algorithm to buy a stock when its 50-day moving average crosses above its 200-day moving average (a bullish signal) and sell when the reverse happens. This approach works well in trending markets but may underperform in sideways or volatile conditions.
3. Market Making
Market-making involves placing simultaneous buy and sell orders at slightly different prices to profit from the bid-ask spread. For example, if the bid price for a stock is ₹500 and the ask price is ₹505, a market maker algorithm might place a buy order at ₹500 and a sell order at ₹505, earning the ₹5 spread. This strategy requires substantial liquidity and works best in highly traded markets.
4. Mean Reversion
Mean reversion strategies assume that prices will revert to their historical average. For instance, if a stock’s price significantly deviates from its average, an algorithm might initiate a buy trade when the price is below the average and sell when it returns to the mean. A practical example includes using RSI (Relative Strength Index) to identify overbought or oversold conditions and automate trades accordingly. This approach is particularly effective in range-bound markets.
How to Get Started with Algo Trading
1. Learn the Basics
Before diving in, educate yourself about trading strategies, technical indicators, and market mechanics. Books like “Algorithmic Trading” by Ernest P. Chan are excellent resources.
2. Choose a Platform
Several platforms in India, such as Zerodha’s Streak, Angel One API, and Upstox API, offer tools for beginners to start algo trading without extensive coding knowledge.
3. Develop or Buy Algorithms
You can either write your own algorithms using programming languages like Python or purchase pre-built strategies from trusted sources.
4. Backtest Your Strategies
Test your algorithm on historical data to ensure it performs well across different market conditions.
5. Start Small
Begin with a small investment and scale up as you gain confidence in your strategies.
Case Study: How Algo Trading Benefited a Retail Investor
While retail-focused platforms like Zerodha’s Streak have enabled individual investors to explore algo trading, there are notable real-world examples of its effectiveness. For instance, Renaissance Technologies, a global hedge fund led by Jim Simons, has famously used algorithmic strategies to deliver unparalleled returns over decades. Though on a much larger scale, this highlights the transformative potential of data-driven trading systems. Retail investors can similarly use smaller-scale strategies to achieve systematic and consistent results.
Regulations for Algo Trading in India
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates algo trading to ensure fairness and transparency. Some key guidelines include:
- Exchange Approval: Algorithms must be approved by stock exchanges.
- Risk Management: Platforms must implement adequate risk controls to prevent market manipulation.
- Transparency: Brokers must provide clear audit trails for algo trades.
Conclusion: Is Algo Trading Right for You?
Algorithmic trading is revolutionizing the way we invest, offering speed, precision, and efficiency. While it comes with challenges like technical complexity and initial costs, the potential benefits make it a worthwhile endeavor for those willing to learn. Whether you’re a retail investor looking to automate your trades or a seasoned professional seeking an edge, algo trading can open up new possibilities in the financial markets.
As technology continues to evolve, the accessibility and effectiveness of algo trading will only improve. So, why not take the first step today and explore the future of investing?
FAQs
- Do I need programming skills for algo trading?
While coding skills are helpful, platforms like Zerodha’s Streak and Tradetron allow beginners to create algorithms without programming. - How much capital is required to start algo trading?
You can start with as little as ₹10,000, but a higher capital base allows for better diversification. - Is algo trading risk-free?
No, like all trading strategies, algo trading involves risks such as market volatility and system failures. - Can I use algo trading for long-term investing?
Yes, algorithms can be designed for both short-term trades and long-term investment strategies.